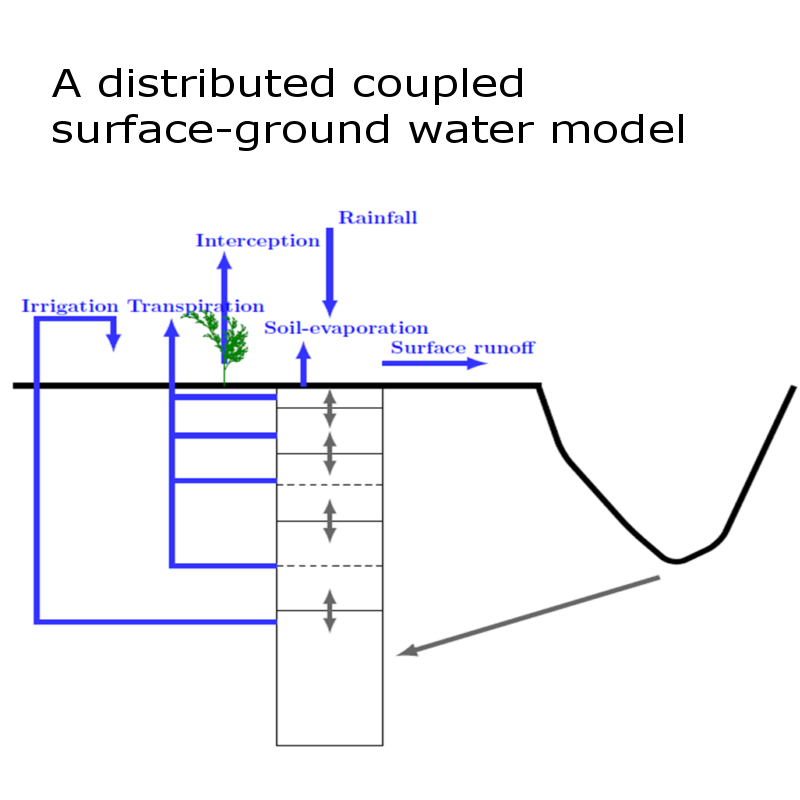
A coupled surface-ground water model was developed, which had 5 layers for the vadose zone and one layer for the ground water zone, in order to consider the major hydrological processes from ground surface to ground water table in a semi-arid watershed. The major aim of this model was to be able to use remotely sensed data of surface soil moisture and evapotranspiration to simulate recharge. The performance of the model was evaluated with the measured watershed average root zone soil moisture and ground water levels. The watershed average root zone soil moisture was obtained by averaging the field measurements from 20 plots and average ground water level was obtained by averaging the field measurement from 200 bore wells. In order to assimilate the AET into the coupled model, the daily AET at a spatial resolution of 1 km was estimated from MODIS data. The AET was validated in one forested and four agricultural sites in the watershed. The validation was based on the comparison with AET simulated from water balance models. It was found that the assimilation helped in capturing the trends in deeper layer soil moisture and ground water level.